Decoupling of barium and silicon at the Congo river-dominated Southeast Atlantic Margin: combined Barium and silicon isotope evidence
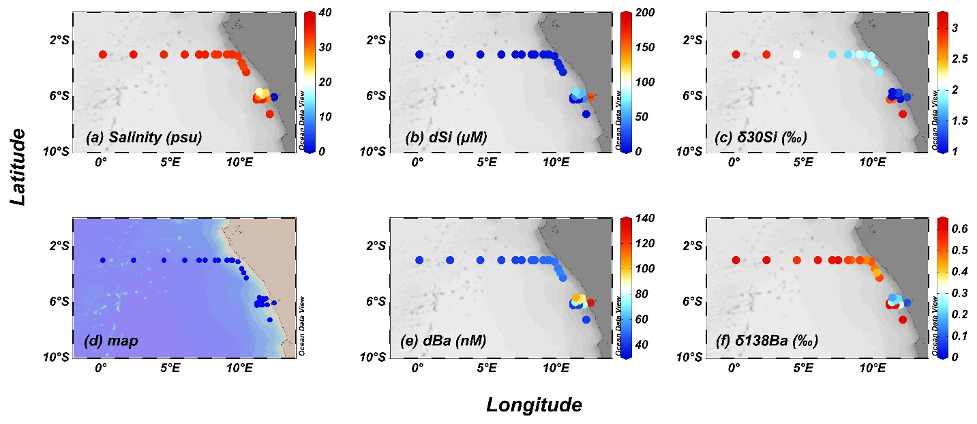
Zhang and co-authors (2023, see reference below) conducted a comprehensive study to investigate the biogeochemical cycles of barium (Ba) and silicon (Si) and their relationship during transport from the Congo River mouth along the southwestern African shelf to the open northern Angola Basin, as part of the GEOTRACES eastern South Atlantic Ocean GA08 cruise (Meteor 121). The study employed a combination of stable Ba (δ138Ba) and Si (δ30Si) isotopes, along with Ba and Si fluxes estimated based on radioactive radium isotopes (228Ra). The authors have observed and demonstrated:
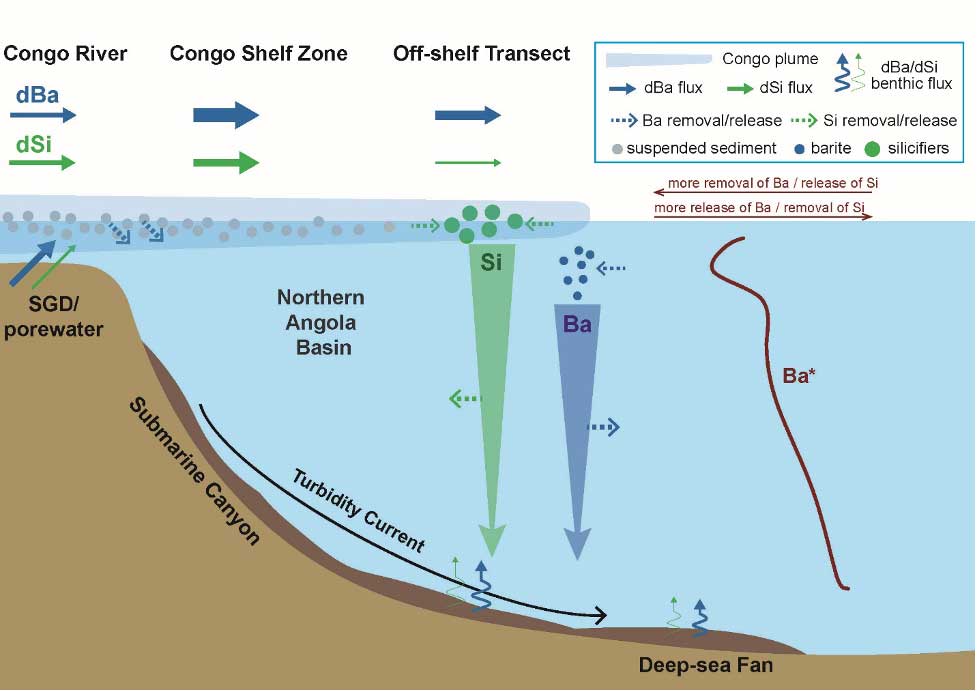
- Stronger enrichment of dissolved barium (dBa) than silicon (dSi) in the shelf-zone of the Congo plume
- Diatom silica production has negligible effect on dissolved Ba isotopic compositions in large river plumes
- Marked dBa enrichment (up to 24 nM) in the deep water of the northern Angola Basin likely originating from high benthic inputs
Their findings reveal a pronounced decoupling of Ba and Si at the Congo River-dominated Southeast Atlantic margin and highlight the strong influence of the margin on marine Ba cycling. Furthermore, their research suggests that the association between concentrations of dissolved Ba (dBa) and Si (dSi) across the global ocean is primarily a consequence of the large-scale ocean circulation.
Reference:
Zhang, Z., Yu, Y., Hathorne, E. C., Vieira, L. H., Grasse, P., Siebert, C., Rahlf, P., Frank, M. (2023). Decoupling of barium and silicon at the Congo River-dominated Southeast Atlantic margin: Insights from combined barium and silicon isotopes. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 37, e2022GB007610, Access the paper: https://doi.org/10.1029/2022GB007610
