Central Arctic fertilization by the Transpolar Drift
Primary production in the Arctic Ocean is often limited by light and nutrient availability due to sea ice coverage. However, the Transpolar Drift (TPD) surface current is conveying ice but also weathering products discharged by rivers along the Siberian coast towards the central Arctic Ocean. Using dissolved and biogenic silica (Si) concentrations and isotopes, Liguori and her colleagues (2021, see reference below) reveal that shelf-derived waters reach far into the central Arctic Ocean and despite sea ice coverage and associated light limitation, diatoms (most likely sea ice attached diatoms) significantly modify dissolved Si concentrations and isotope ratios of the surface waters. Such findings highlight the importance of the TPD in delivering dissolved silica and iron to feed low, but still present, diatom primary production in the central Arctic Ocean. Outside the TPD influence, surface stratification limits iron and nutrient supply to the surface, leading to limited primary production at the time of sampling. Due to the effects of climate warming leading to increasing river discharge and decreasing sea ice coverage in the Arctic, the increase in nutrient supply as well as alleviation of light limitation under the TPD influence are likely to have a strong impact on primary production in the future.
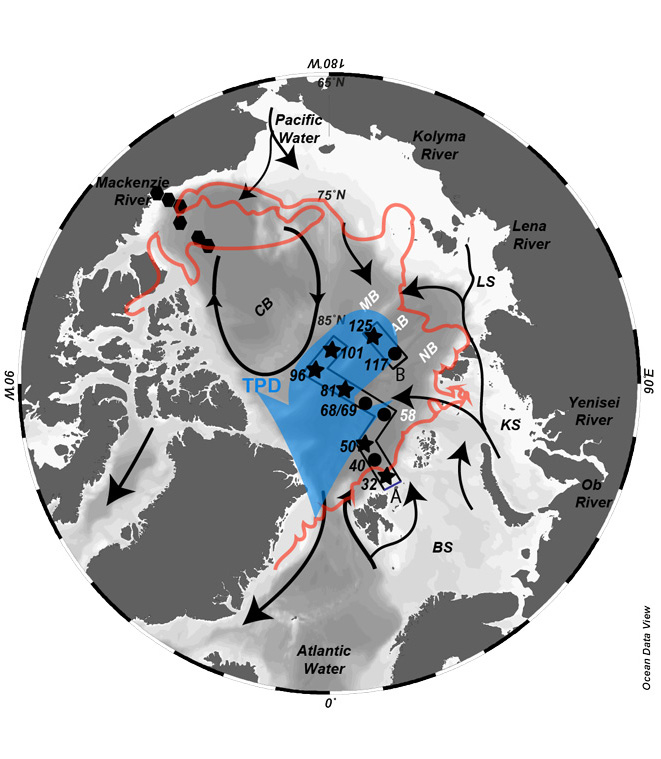
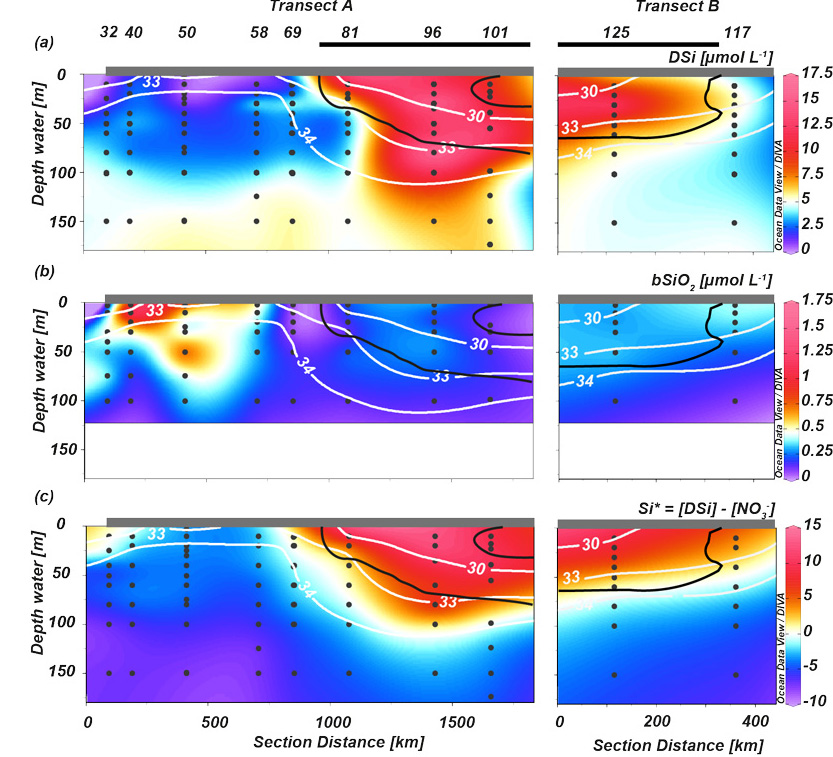
Figure: Map showing the location of the sampling stations divided into transect A and B. Blue arrow highlights the TPD location (also shown by solid black lines on right panels). The right panels show contrasting conditions outside and under the TPD influence, which higher dissolved silica concentrations (a) and lower biogenic silica concentrations (b) are determined under the TPD influence. These findings, combined with dissolved and biogenic silica isotopes, highlight the importance of the TPD in feeding the central Arctic Ocean primary production, mainly diatoms, due to the non-limiting conditions in regard to dissolved silica represented by Si* (c).
Reference:
Liguori, B. T. P., Ehlert, C., Nöthig, E., Ooijen, J. C., & Pahnke, K. (2021). The Transpolar Drift Influence on the Arctic Ocean Silicon Cycle. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 126(11). Access the paper: 10.1029/2021jc017352
