Quantifying the weathered fluxes to the ocean is far from over: the overlooked role of rock coast erosion
This study reveals that cliff derived sediment supply is only three times less than the solid discharge of rivers for Europe.
This section presents the GEOTRACES scientific activities.


This study reveals that cliff derived sediment supply is only three times less than the solid discharge of rivers for Europe.
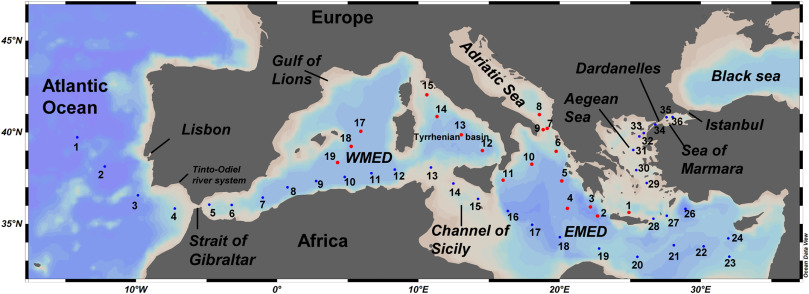
Extensive trace metal clean sampling during the Dutch GEOTRACES cruise in the Mediterranean Sea allowed Middag and his colleagues to establish the basin scale distribution of these trace metals.
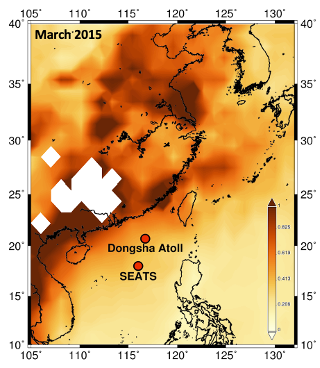
Liao and colleagues determined zinc concentrations and isotope compositions in sinking particles collected in the Northern South China Sea…
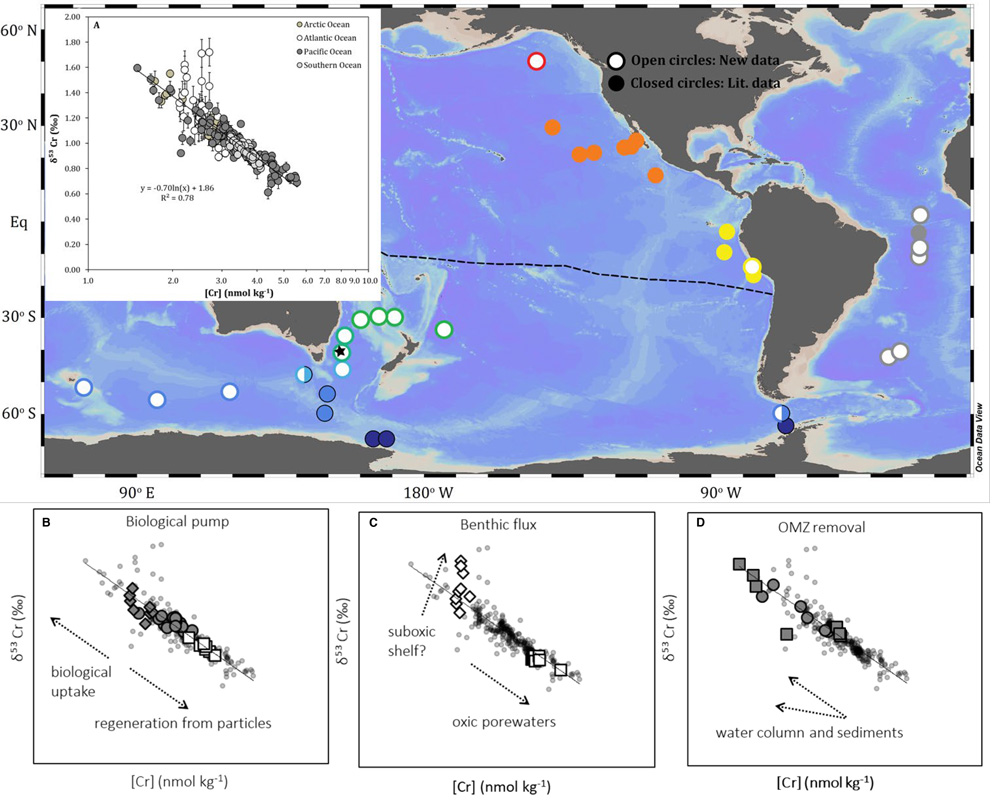
Janssen and co-authors present an exhaustive compilation of ocean chromium data…
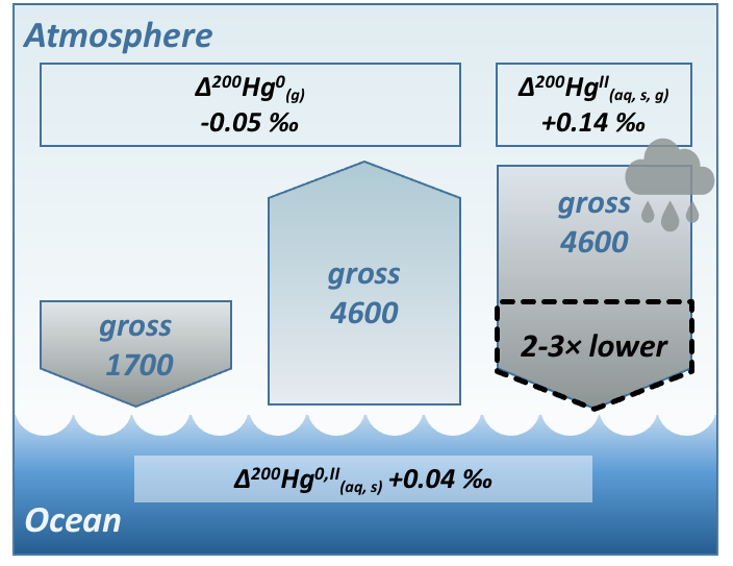
The study’s results hold promise that the implementation of anti-pollution measures under the Minamata Convention will likely result in a faster decrease of oceanic mercury levels than previously thought.
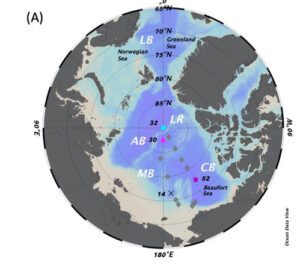
This study challenges the paradigm that dissolved aluminium in the bottom waters of the Arctic basins could result from a top-down process.
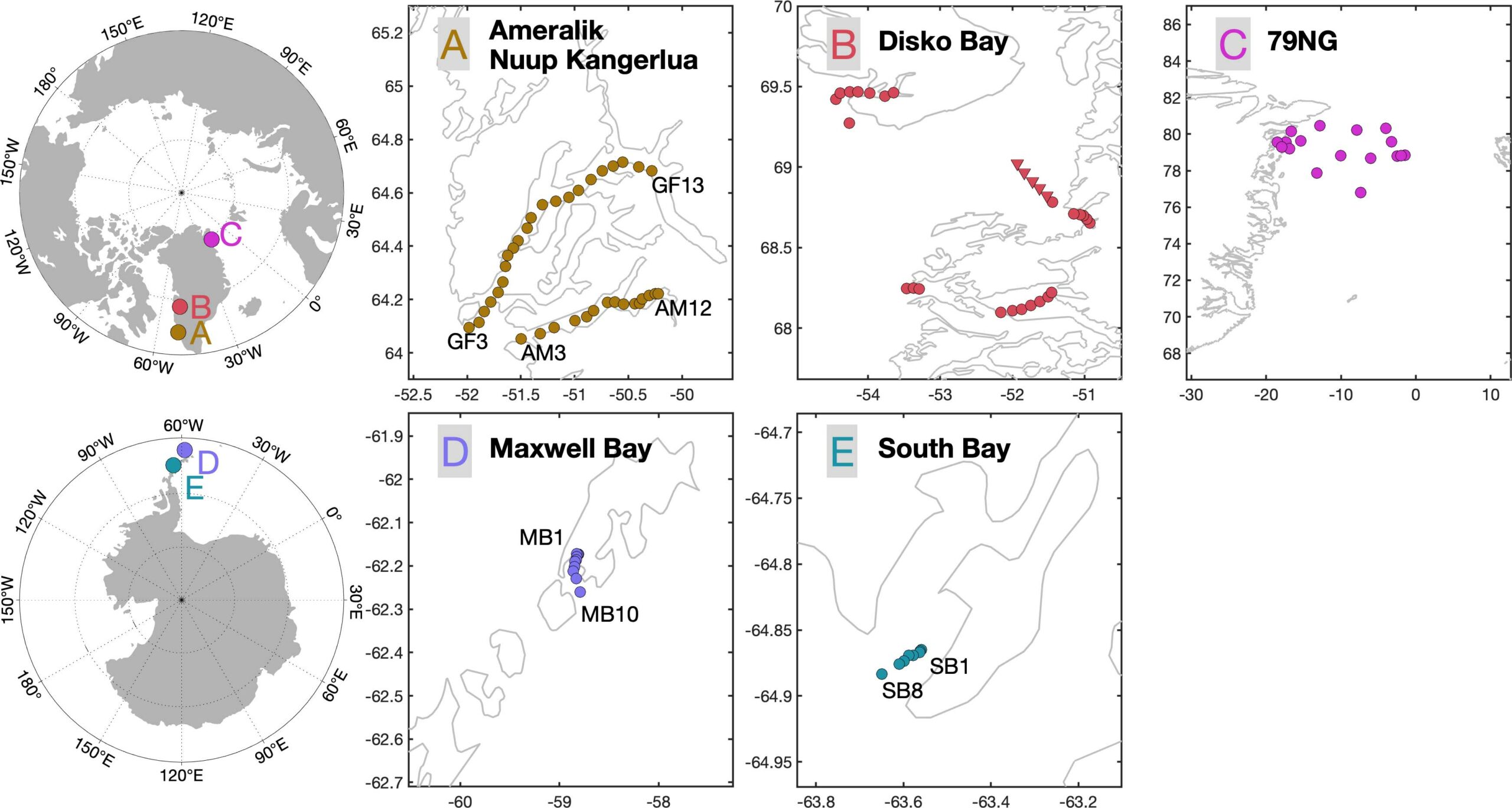
Earth’s Ice Sheets are known to release significant quantities of lithogenic particles into the ocean every year, but how does this material affect trace metal availability in the ocean?
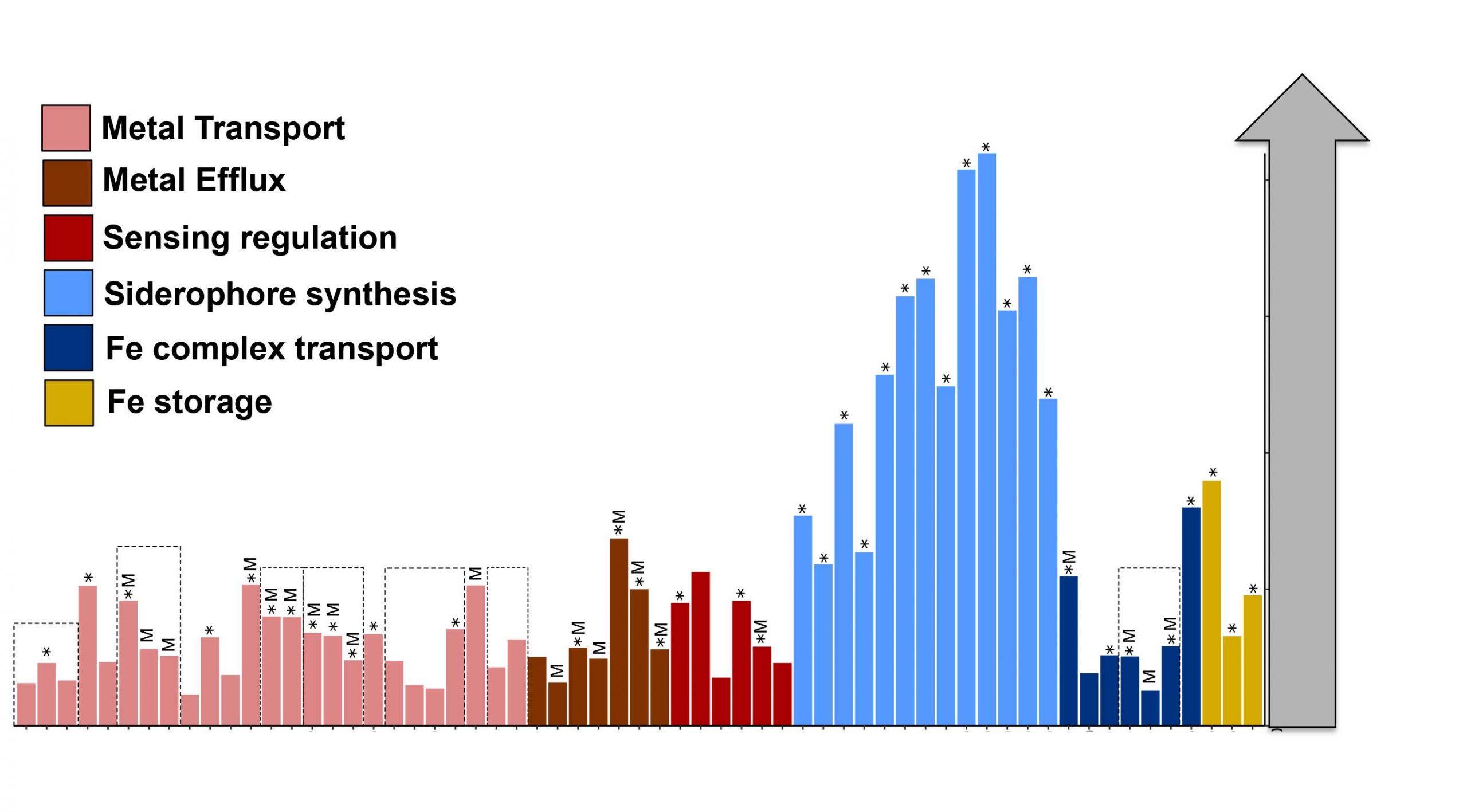
This study provides evidence for the processing of nine particulate trace metals in multiple manners by diverse microbial communities.
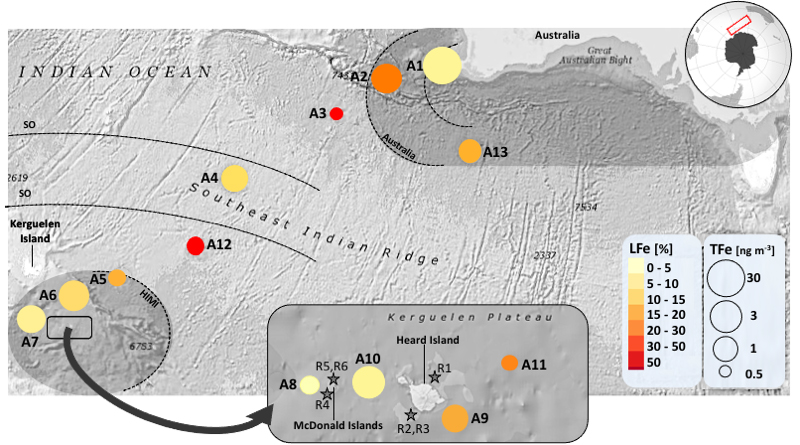
This study suggests that volcanic emission can represent a significant source of bioavailable iron to open ocean anaemic ecosystems.